|
Haode Zhang 张皓德 I am a fourth-year undergraduate student at Shanghai Jiao Tong University, majoring in Mechanical Engineering. I'm currently working with Prof. Ruohan Gao and Ph.D. mentor Kelin Yu at UMD. I was also fortunate to work with Prof. Wanxin Jin from ASU and Prof. Yong-Lu Li from SJTU during my undergraduate. |

|
Research Interests
My research interests lie in robot learning, learning-based control and human-robot interaction.
I want to build human-centered robots, robots that can: I am currently seeking a Ph.D. opportunity for Fall 2026 in robotics! |
News
[Jan. 2026] BSV is accepted to ICLR 2026. |
Publications
|
|
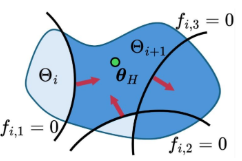
Zhixian Xie*, Haode Zhang*, Yizhe Feng, Wanxin Jin ICML, 2025 project page / paper / code We propose a novel geometric view of reward alignment as an iterative cutting process over the hypothesis space. Our batched cutting method significantly improves data efficiency by maximizing the value of each human preference query. We introduce a conservative cutting algorithm that ensures robustness to unknown erroneous human preferences without explicitly identifying them. |
|
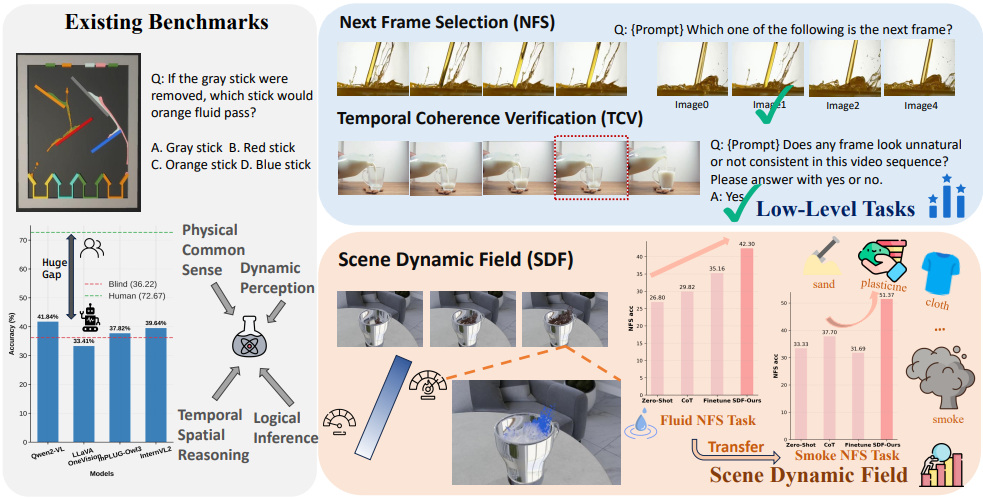
Nanxi Li, Xiang Wang, Yuanjie Chen, Haode Zhang, Hong Li, Yong-Lu Li ICLR, 2026 We propose Scene Dynamic Field (SDF), a cost-efficient framework that integrates physics simulators into multi-task fine-tuning, substantially improving MLLMs’ intuitive physics understanding and achieving strong generalization across physical domains. |
|
The website is built upon this template. |